Industrial Fanless Design
Industrial Technology
2020/01/18
What is a Fanless System
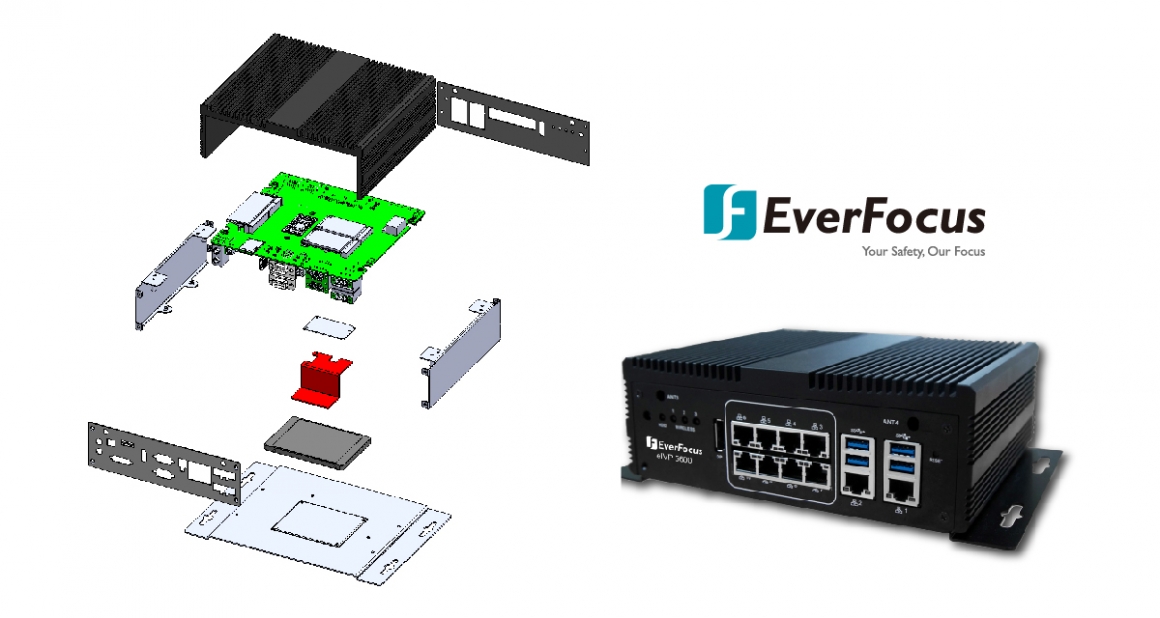
Fanless systems utilize a heatsink, which allows for the heat generated within the system to move through the heat spreading element and dissipate away from the system.
Normally comprised of copper or aluminum, heatsinks are used in many electronic
devices from smartphones to refrigerators because of their ability to cool components that encounter performance degradation caused by increased temperatures. Physically they appear with fins protruding from a base increasing the surface area to improve heat transfer. In a fanless system, a heatsink is normally attached directly to the CPU and in most cases is an integral part of the chassis of the system. Heat is transferred from the CPU through the fins on top of the passive heatsink which then guides the heat allowing it to radiate to the surrounding air. This effective construction and its obvious benefits have added to the appeal and subsequent adoption of fanless systems in a myriad of applications crossing over multiple industries and IoT applications, including Factory Automation, Retail Intelligence, Instrumentation, and Medical device gateway.
One of the challenges when designing a rugged computer system is to deliver a product that meets the performance requirements while operating in harsh environments over a wide range of temperatures. The challenge to meet these requirements is made greater when durability and elimination of moving parts becomes a primary consideration.
Benefits Of Fanless Systems
Fanless systems offer a number of key advantages over traditional systems with active cooling and also excel in harsh environments.
Silent Operation
This obvious benefit comes by way of reduction of audible noise from fans. Anyone that has walked through a data center housing a large population of servers mounted in rack enclosures is aware of how loud fans operate, often drowning out verbal communication amongst personnel performing work in these rooms. Silent operation is an important consideration for applications require noise-free environment such as hospitals, laboratories, schools and libraries.
Wide Operating Temperature
With a solid thermal design, fanless systems dissipate heat more efficiently and
demonstrate a wider operating temperature in many industrial IoT applications.
Components are chosen for their extended temperature range allowing the fanless
system to operate within a much wider thermal envelope, ranging from -20°C to 60°C.
Fanless systems utilize a heatsink, which allows for the heat generated within the system to move through the heat spreading element and dissipate away from the system.
Normally comprised of copper or aluminum, heatsinks are used in many electronic
devices from smartphones to refrigerators because of their ability to cool components that encounter performance degradation caused by increased temperatures. Physically they appear with fins protruding from a base increasing the surface area to improve heat transfer. In a fanless system, a heatsink is normally attached directly to the CPU and in most cases is an integral part of the chassis of the system. Heat is transferred from the CPU through the fins on top of the passive heatsink which then guides the heat allowing it to radiate to the surrounding air. This effective construction and its obvious benefits have added to the appeal and subsequent adoption of fanless systems in a myriad of applications crossing over multiple industries and IoT applications, including Factory Automation, Retail Intelligence, Instrumentation, and Medical device gateway.
One of the challenges when designing a rugged computer system is to deliver a product that meets the performance requirements while operating in harsh environments over a wide range of temperatures. The challenge to meet these requirements is made greater when durability and elimination of moving parts becomes a primary consideration.
Benefits Of Fanless Systems
Fanless systems offer a number of key advantages over traditional systems with active cooling and also excel in harsh environments.
Silent Operation
This obvious benefit comes by way of reduction of audible noise from fans. Anyone that has walked through a data center housing a large population of servers mounted in rack enclosures is aware of how loud fans operate, often drowning out verbal communication amongst personnel performing work in these rooms. Silent operation is an important consideration for applications require noise-free environment such as hospitals, laboratories, schools and libraries.
Wide Operating Temperature
With a solid thermal design, fanless systems dissipate heat more efficiently and
demonstrate a wider operating temperature in many industrial IoT applications.
Components are chosen for their extended temperature range allowing the fanless
system to operate within a much wider thermal envelope, ranging from -20°C to 60°C.
- Top heatsink contact CPU & Memory for the thermal dissipation
- Customization carrier board for vertical markets
- Support 7mm or 9mm height cableless SATA SSD
- Support antennas for wireless communication




